Understanding of spatial and temporal distribution of turbulence structure in the troposphere is important for improving the performance of numerical weather prediction and climate models. It is also important to model clear air turbulence as that would aid in limiting the air traffic disasters, particularly over the complex mountainous regions. Characterization of turbulence in the mountainous region is vital to understand the dynamics of mountain induced wave perturbations and other mesoscale phenomena which have a crucial role in modulating the general circulation wind patterns.
Scientists at the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India have estimated turbulence parameters in the lower troposphere over the central Himalayan region for the first time.
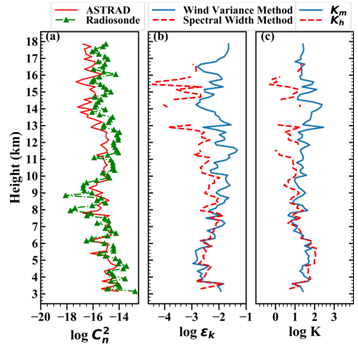
The researchers have calculated the magnitude of refractive index structure (Cn2) a constant that represents the strength of the atmospheric turbulence using observation from their Stratosphere Troposphere Radar (S T Radar). In the study published in Radio Science journal led by Aditya Jaiswal, a PhD student at ARIES Nainital and ARIES faculties D.V. Phani Kumar, S. Bhattacharjee and Manish Naja have found that refractive index structure constant (Cn2), is as large as 10-14 m-2/3. Such large values at the lower altitudes are due to the mountain wave activities and presence of low level clouds.The Low level clouds are generated in mountainous regions having complex topography. Because of this, stable air in this region is set into oscillations known as mountain waves and lee waves. While the turbulence parameters for southern India was known earlier, the same were not known over the Himalayan regionThe Low level clouds are generated in mountainous regions having complex topography. Because of this, stable air in this region is set into oscillations known as mountain waves and lee waves. While the turbulence parameters for southern India was known earlier, the same were not known over the Himalayan region.

The S T Radar utilised in this study uses Doppler effect to measure wind velocities, detect gusts and the turbulence in the clear air. The present radar is configured as an active aperture phased array using solid state based Transmit and Receive Modules and Digital Signal Processing techniques. The phased array system contains 588 three element Yagi-Uda antennae arranged in the Quasi Circular Aperture Equilateral Triangle Grid. The array is divided in 12 clusters, with each cluster containing 49 elements arranged in hexagon pattern.
This radar project was funded by the SERB, DST, Government of India and developed within the country.
Coverage of ST Radar results in the Print and Electronic Media
- Press Information Bureau
- Vigyan Samachar (Vigyan Prasar)
https://vigyanprasar.gov.in/wpcontent/uploads/vigyansamachardst0211Sep2020.pdf
- DD News
- Financial Express
- Times of India
- The Tribune
https://m-tribuneindia-com.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/m.tribuneindia.com/news/nation/for-first-time-scientists-work-out-turbulence-parameters-over-himalayas-140264?amp_js_v=0.1&usqp=mq331AQFKAGwASA%3D&fbclid=IwAR0t9QChdxhRT9SzSkupXtUE_wlHjTmGpirVhcs-hA_tGkIhVRt1vLbMtkE#origin=https://www.google.com&cid=1&prerenderSize=1&visibilityState=visible&paddingTop=32&history=1&p2r=0&csi=1&storage=1&viewer
- Outlook India
- Deccan Herald
- NDTV
- News18
- IndiaTV
- APAC Digital News Network.com
- Amar Ujala
- Dainik Jagaran
- Today News
- Greater Kashmir
- Asian News Service
http://asiannewsservice.in/en/national/atmospheric-turbulence-parameters/
- The News Now
http://www.thenewsnow.co.in/newsdet.aspx?q=115039
- The News Tube
https://newstube.co.in/scientists-estimate-turbulence-parameters-over-central-himalayas/

